In today’s hyper-connected world, integration is the backbone of digital transformation. Whether it’s linking CRM with ERP, connecting e-commerce platforms to warehouse systems, or enabling real-time event-driven workflows, the ability to connect systems reliably and intelligently is no longer optional — it’s strategic.
But integration is not just about connecting endpoints — it’s about doing it right. This is where Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIPs) come in.
What Are Enterprise Integration Patterns?
Originally published by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolf in the book Enterprise Integration Patterns, these patterns provide proven solutions to common integration problems.
They are language-agnostic architectural building blocks that help in designing robust, maintainable, and reusable integration solutions.
🔁 Think of them as the “design patterns” for system integration.
Why Should Architects and Organizations Care?
✅ Architects
- Use these patterns to define integration strategies aligned with business goals.
- Design solutions that are scalable, observable, and secure.
- Enable standardization across projects.
✅ Organizations
- Avoid reinventing the wheel for each integration use case.
- Improve agility in connecting SaaS platforms, on-prem systems, and cloud services.
- Enhance system reliability with standardized error handling, retries, throttling, and monitoring.
Benefits of Using Integration Patterns
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reusability | Reuse patterns across teams, projects, and domains. |
| Clarity of Design | Make your designs explicit, readable, and well-documented. |
| Standardization | Promote consistency across integration implementations. |
| Operational Robustness | Patterns like Retry, Circuit Breaker, and Store-and-Forward improve uptime. |
| Improved Observability | Correlation IDs, Wire Taps, and Monitoring flows increase system visibility. |
| Testability | Patterns like Test Message and Message Store allow for robust testing setups. |
Azure + EIPs: A Perfect Match
With modern cloud-native tools like Azure Logic Apps, Azure Functions, Service Bus, API Management, Blob Storage, and Event Grid, Microsoft Azure provides everything you need to implement EIPs at scale and with ease.
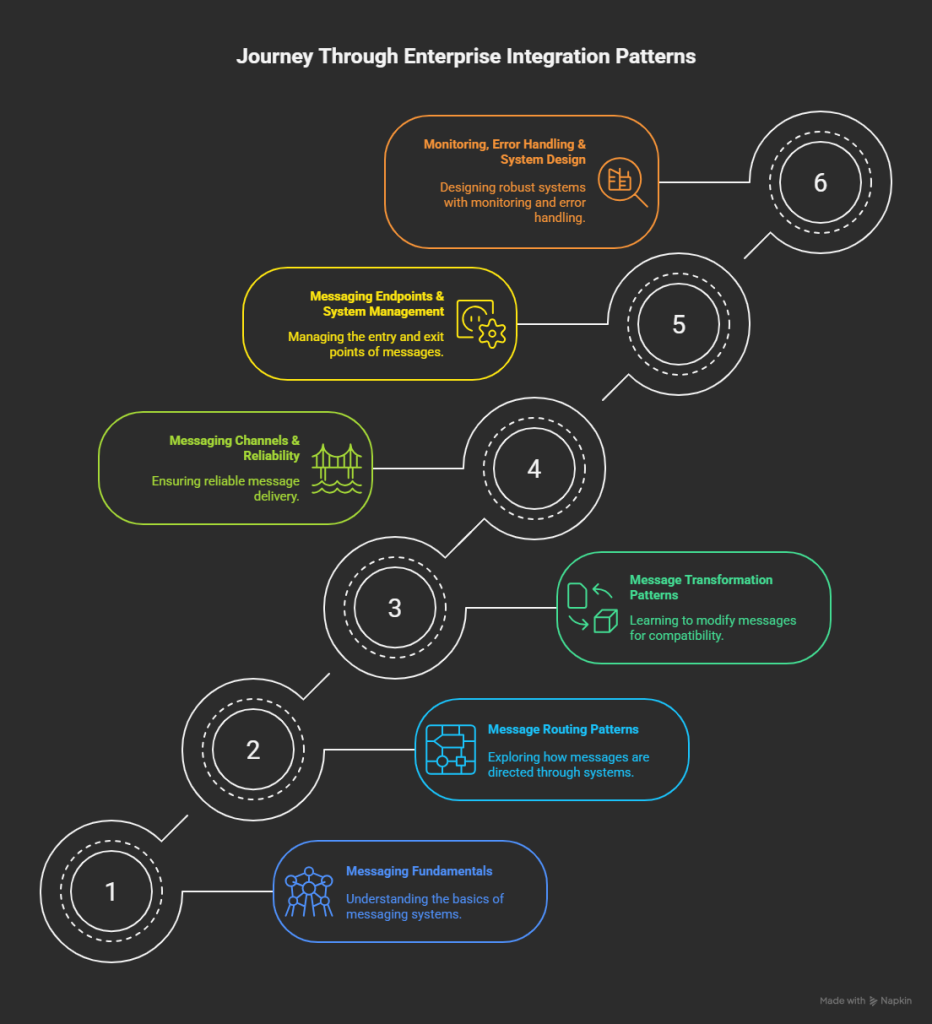
This blog series will walk you through all 65 Enterprise Integration Patterns, showing you how to implement each one using Azure Integration Services.
The Blog Series: Azure-Enabled EIP Implementation
Here’s what we’ve covered (and what’s coming):
Part 1: Messaging Fundamentals
Understand the basics — Message, Channel, Endpoint, Translator, Filter, Claim Check, Envelope Wrapper.
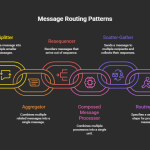
Part 2: Routing Patterns
Learn how to direct traffic — Content-Based Router, Splitter, Aggregator, Resequencer, Recipient List.
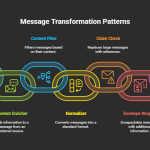
Part 3: Transformation Patterns
Format conversions and semantic alignment — Canonical Data Model, Normalizer, Content Enricher, Translator.
Part 4: Messaging Channels & Reliability
Build reliable messaging infrastructure — Point-to-Point, Pub/Sub, DLQ, Guaranteed Delivery.
Part 5: Messaging Endpoints & System Management
Where integrations connect — Service Activators, Event Consumers, Smart Proxies, Control Bus.
Part 6: Error Handling & Monitoring Patterns
Resilience and visibility — Retry, Circuit Breaker, Throttling, Correlation, Store and Forward.
Who Should Read This Series?
✅ Integration Architects
✅ Solution Designers
✅ DevOps Engineers
✅ Cloud & API Developers
✅ Anyone connecting applications, services, and data across the enterprise.
Format for Each Pattern:
- ✅ Scenario (When to Use)
- 🔄 End-to-End Flow
- ⚙️ Component Roles
- 🛠 Azure Implementation
- 📈 Visual Flow Diagram (in Markdown or image)
Complete Reference Table
This table provides a comprehensive view of all 65 Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIPs) with their relevance, use cases, Azure Integration Services implementations, and practical flow. Each row offers a condensed yet detailed reference, making it easy for architects and developers to apply the right pattern in real-world scenarios.
| # | Pattern | Scenario | Use Case | Azure Implementation | Flow Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Message | Encapsulates data being transferred | Order info sent from website to ERP | Service Bus Message with custom headers, Logic App picks up and posts to ERP | Web App → Service Bus → Logic App → ERP |
| 2 | Message Channel | Logical conduit for message delivery | Billing system sends invoice requests to print service | Service Bus Queue or Topic | Billing App → Queue → Print Service |
| 3 | Message Endpoint | Interface to send/receive messages | Support app receives tickets via endpoint | API Management + Logic App + Service Bus | External App → APIM → Logic App → CRM |
| 4 | Message Router | Directs messages to destination | Route product updates to shipping/inventory systems | Logic App with Switch or Service Bus Topic Filters | Product Message → Logic App → Queue A/B/C |
| 5 | Message Translator | Converts message format/schema | XML claim → JSON API | Logic App @xml() and json() or Liquid templates | Partner A → Logic App → Partner B |
| 6 | Message Filter | Filters messages before processing | Transactions above €1,000 for fraud check | Logic App Condition or Service Bus Subscription Filters | Incoming → Filter → Qualify or Drop |
| 7 | Envelope Wrapper | Wraps data with metadata | Add tracking ID, versioning, auth | Compose in Logic App + Key Vault for tokens | Message → Envelope → Queue |
| 8 | Claim Check | Stores payload externally, passes reference | Share large file via SAS URL | Blob Storage + Logic App → Queue with URL | Upload → Blob + URL → Queue → Download |
| 9 | Content Filter | Removes unnecessary data | Remove PII before processing | Logic App Select, Function App, config-based | Message In → Filter Out → Clean Message |
| 10 | Normalizer | Unifies varied message formats | Orders from multiple vendors → standard format | Logic App Switch, Liquid templates | Vendor → Normalizer → Processor |
| 11 | Canonical Data Model | Standardized internal model | CRM/ERP systems speak different schemas | Azure Functions, Logic App transformations | External → Canonical Model → Internal |
| 12 | Pipes and Filters | Compose processing logic into filters | Transform, validate, route messages | Logic Apps with chained steps | In → Step1 → Step2 → Out |
| 13 | Message Broker | Central mediator to route/control | Central message control point | Azure Service Bus or Event Grid | App → Broker → Subscriber |
| 14 | Event Message | Notification-style message | New order event triggers inventory update | Event Grid/Event Hub | Source → Event Grid → Logic App |
| 15 | Command Message | Instruction for receiver to act | “Generate Invoice” request | Service Bus Queue or API trigger | Sender → Queue/API → Action Handler |
| 16 | Document Message | Carries complete business document | Invoice PDF sent to processor | Blob/Service Bus → Logic App | Uploader → Blob + Metadata → Processor |
| 17 | Request-Reply | Sync communication pattern | App requests shipment status | API Management + Response Logic | App → Request → Logic App → Response |
| 18 | Return Address | Specifies reply channel | Logic App includes reply-to URL | Include ReplyTo header | API Call → Logic App → ReplyTo |
| 19 | Correlation Identifier | Tracks related messages | Trace flow across services | Use correlation ID in header | Message → Multi Services → Trace ID |
| 20 | Message Sequence | Order within message batch | Batch of logs sent in sequence | Message ID + Sequence Number | Batch → Logic App → Reorder |
| 21 | Message Expiration | Auto-expiry of stale messages | Ignore messages older than X mins | TimeToLive in Service Bus | Queue → Expire → Dead-letter or Drop |
| 22 | Format Indicator | Identifies schema type | Payload includes format tag | Header or property flag | Parser uses tag to choose logic |
| 23 | Message Dispatcher | Routes messages to consumer threads | Parallel processing of orders | Service Bus Topics with subs | Queue → Dispatcher → Multiple Receivers |
| 24 | Message Endpoint | Repeated: Interface to messaging infra | See #3 | API Management / Logic App | |
| 25 | Durable Subscriber | Retains messages while offline | Subscription model with persistence | Service Bus Topic + Subscription | Event Source → Topic → Sub |
| 26 | Idempotent Receiver | Handles duplicate messages safely | Prevent reprocessing same order | Store MessageID and dedup logic | Receiver checks ID before processing |
| 27 | Service Activator | Activates service on message arrival | New message triggers processor | Logic App/Function triggers | Queue → Trigger → Processor |
| 28 | Splitter | Breaks message into parts | Split multi-invoice batch | For-each in Logic App | Batch → Split → Process each |
| 29 | Aggregator | Merges parts into one | Combine multiple responses into report | Logic App with correlation | Parts → Wait → Merge → Output |
| 30 | Resequencer | Reorders messages | Ensure message order integrity | Durable storage + sort logic | Msgs → Store → Sort → Send |
| 31 | Composed Message Processor | Parallel processing of sub-messages | Process sub-tasks separately | Parallel Logic App branches | Split → Parallel → Combine |
| 32 | Routing Slip | Dynamic routing path | Message defines its own journey | Logic App or Function reads route | Read Route → Call Services → Track |
| 33 | Process Manager | Orchestrates message flow | Stateful multi-step flow | Durable Functions / Logic App | Start → Step1 → Step2 → End |
| 34 | Wire Tap | Monitor message without affecting it | Debug/observe in-flight message | Logic App clone flow → monitor | Message → Branch → Monitor + Main |
| 35 | Message History | Track full message path | Audit trail | Append tracking metadata | Log every hop |
| 36 | Message Store | Persist messages for replay/debug | Archive messages for compliance | Azure Blob or CosmosDB | Receive → Store → Replay/Inspect |
| 37 | Smart Proxy | Adds value while forwarding | API gateway adds auth + metrics | APIM → Logic App → Backend | Request → Proxy → Backend |
| 38 | Test Message | Test system without real payload | Send dummy messages | Postman / Logic App with sample data | Test → System → Result |
| 39 | Channel Adapter | Connect system to messaging infra | SAP sends messages to Service Bus | Connector or custom Function | App → Adapter → Service Bus |
| 40 | Messaging Gateway | Central entry point | One endpoint to access multiple systems | APIM routes to backend | Client → Gateway → System A/B/C |
| 41 | Transactional Client | All-or-nothing message logic | Send + Store transaction in sync | Azure Transaction Scope | Client → Txn → Commit or Rollback |
| 42 | Polling Consumer | Actively fetch messages | Logic App with interval trigger | Timer → Poll → Process | |
| 43 | Event-Driven Consumer | Reacts to message event | Trigger on event | Event Grid → Logic App trigger | |
| 44 | Competing Consumers | Parallel consumers for scaling | Multiple functions on same queue | Queue → Competing Functions | |
| 45 | Message Dispatcher | See #23 | |||
| 46 | Selective Consumer | Chooses message type to consume | Filter logic on receiver | Topic Subscription Rule | Topic → Sub A (type = x), B (type = y) |
| 47 | Durable Subscriber | See #25 | |||
| 48 | Message Bus | Decentralized event distribution | Event mesh | Azure Event Grid / Event Hub | Publisher → Event Bus → Consumers |
| 49 | Transactional Messaging | Message & DB changes atomic | Update DB and queue in one txn | Azure Transaction Support | Txn Begin → Msg + DB → Commit |
| 50 | Messaging Bridge | Connects two message systems | Kafka ↔ Service Bus | Azure Function bridge | System A → Bridge → System B |
| 51 | Message Tunnel | Encapsulate cross-boundary message | Secure internal → external | APIM, encryption, identity | Intranet → Tunnel → External System |
| 52 | Control Bus | Infra management messages | Monitor configs, metrics | Telemetry channel | Monitor → Control Channel → Admin Tool |
| 53 | Detour | Redirect flow temporarily | Reroute due to system upgrade | Logic App with feature flag | Route A → Route B (temp) |
| 54 | Invalid Message Channel | Route failed messages | Handle poison messages | Service Bus DLQ or retry queue | Queue → DLQ |
| 55 | Dead Letter Channel | Store unprocessable messages | Messages that fail all retries | Service Bus DLQ | Retry → Fail → DLQ |
| 56 | Compensation Transaction | Undo previous action | Cancel order after payment | Logic App with undo branch | Txn → Fail → Compensate |
| 57 | Retry Pattern | Retry transient errors | Retry API if timeout | Logic App retry policy | Try → Retry (x times) → Success/Fail |
| 58 | Timeout Pattern | Avoid indefinite waiting | Timeout on long API call | Logic App timeout setting | Call → Wait (max X sec) → Abort |
| 59 | Circuit Breaker | Protect downstream system | Stop calling failing API | APIM policy or Function flag | Failure Rate High → Open Circuit |
| 60 | Bulkhead Pattern | Isolate failures | Separate execution pools | Logic App isolation per service | A fail ≠ B fail |
| 61 | Throttling | Limit call rate | Prevent API overuse | APIM throttle policy | Request → Limit N/sec |
| 62 | Load Leveling | Smooth workload spikes | Queue between sender and processor | Service Bus decouples | Spiky Load → Queue → Smooth Consume |
| 63 | Priority Queue | Prefer urgent messages | High-priority messages first | Service Bus with priority field | Priority = High → First Processed |
| 64 | Delayer | Delay message delivery | Wait before retrying | Logic App delay action | Wait 30s → Retry |
| 65 | Scheduler | Send message at specific time | Scheduled reminders | Logic App Recurrence | Timer → Trigger → Action |
Each pattern in the table aligns with the Azure-native design philosophy and helps you integrate systems reliably, securely, and at scale.
🎯 Final Thoughts
Whether you’re migrating from BizTalk, building on Azure from scratch, or trying to modernize legacy system interactions, Enterprise Integration Patterns give you the clarity and structure needed to build integrations that last.
Let’s dive in and explore how these powerful patterns come alive on Azure.