In this third post of our blog series on Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIPs) implemented with Azure Integration Services, we explore Transformation Patterns — designs that enable different systems to exchange and understand data by reshaping message content.
These patterns are vital when integrating across multiple vendors, partners, or internal services that use different formats or standards. Common applications include:
- Format conversion between XML and JSON
- Data normalization across partner APIs
- Content enrichment using lookups
- Masking or redacting PII before transmission
Each pattern is structured for WordPress use with:
- ✅ Scenario
- 📘 Use Case
- 🔄 End-to-End Flow
- ⚙️ Component Roles
- 🛠 Azure Implementation
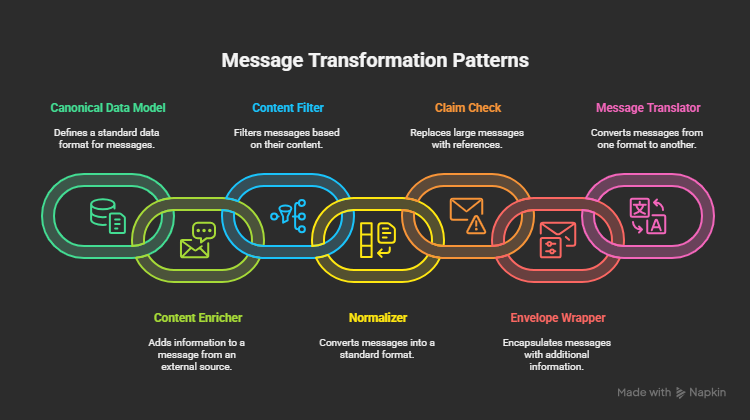
📦 1. Canonical Data Model
✅ Scenario: Converts diverse data formats into a common model to simplify integration.
📘 Use Case: A financial services app receives loan applications from multiple banks in different schemas and transforms them into a unified loan format.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Receive data from source
- Detect schema
- Map to standard canonical model
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App / Function App: Executes transformation logic
- Blob Storage: Stores mapping templates
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Bank A/B/C API] → [Logic App → Map to Canonical Loan] → [Loan Processor API]➕ 2. Content Enricher
✅ Scenario: Adds additional data to a message by calling external services or databases.
📘 Use Case: A package shipment request includes a destination zip code. The system enriches it with city, region, and tax zone using a geo API.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Receive message
- Lookup additional metadata
- Merge and send enriched message
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App / Function App: Calls enrichment services
- External API: Provides reference data
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Shipment Request] → [Logic App]
└──> [Geo API] → [Enriched Request → ERP]🧹 3. Content Filter
✅ Scenario: Removes unnecessary or sensitive data before further transmission.
📘 Use Case: A healthcare integration pipeline removes patient SSN before sending records to third-party processors.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Receive message with PII
- Remove sensitive fields
- Send safe data forward
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Function App: Applies filtering rules
- Logic App: Executes transformation
🛠 Azure Implementation:
Input: { "SSN": "123-45-6789", "Name": "John Doe" }
Output: { "Name": "John Doe" }🛂 4. Claim Check
✅ Scenario: Offloads bulky message content to external storage and sends only a reference (claim check).
📘 Use Case: An insurance system sends claim metadata via message but stores claim documents in Blob Storage.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Upload large files to blob
- Generate SAS URL
- Send metadata + URL via queue
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Blob Storage: Stores files
- Logic App: Generates claim check
- Receiver App: Uses SAS to download content
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Uploader] → [Blob Storage]
→ [Message with SAS URL] → [Receiver retrieves document]🧼 5. Normalizer
✅ Scenario: Aligns different inbound formats to a common structure for downstream processing.
📘 Use Case: A SaaS analytics engine receives user feedback from multiple frontend apps in different formats and normalizes them for reporting.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Detect format type
- Map to standard schema
- Store in central DB or queue
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Function App: Executes conditional mapping
- Logic App: Routes and stores results
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[App A/B/C Feedback] → [Function App → Normalize]
→ [Storage Account / SQL / Queue]🔄 6. Envelope Wrapper
✅ Scenario: Wraps the core message inside an envelope with additional metadata (auth, version, tracking).
📘 Use Case: A logistics system wraps each shipment event in a standard envelope with tracking ID and version before sending to partners.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Prepare base message
- Attach header and metadata
- Send enriched envelope
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Builds envelope structure
- Function App: Adds security/auth headers
🛠 Azure Implementation:
{
"Envelope": {
"Header": {
"AuthToken": "Bearer xyz",
"TrackingId": "SHIP123",
"Version": "v1.0"
},
"Body": {
"ShipmentId": "S001",
"Destination": "Amsterdam"
}
}
}🔃 7. Message Translator
✅ Scenario: Converts message from one format to another (e.g., XML to JSON).
📘 Use Case: A supply chain integrator receives vendor invoices in XML and converts them to JSON for ERP processing.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Receive XML invoice
- Apply transformation logic
- Send to ERP in JSON
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Uses xml() and json() expressions
- API Management: Supports format negotiation
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Vendor XML Invoice] → [Logic App (XML → JSON)] → [ERP API]👉 Up next: Part 4 – Messaging Channels & Endpoints, covering topics like Durable Subscribers, Idempotent Receiver, Point-to-Point Channel, and more.
Stay tuned as we continue breaking down all 65 integration patterns using Azure-native services!