In this second post of our blog series on Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIPs) implemented using Azure Integration Services, we explore Routing Patterns — designs that determine where, how, and to whom a message should be sent.
Routing is a fundamental aspect of distributed system design. These patterns are commonly used in:
- Multi-department order fulfillment
- Vendor-specific message delivery
- Workflow engines
- Asynchronous orchestration pipelines
Each pattern is structured for WordPress as:
- ✅ Scenario
- 📘 Use Case
- 🔄 End-to-End Flow
- ⚙️ Component Roles
- 🛠 Azure Implementation
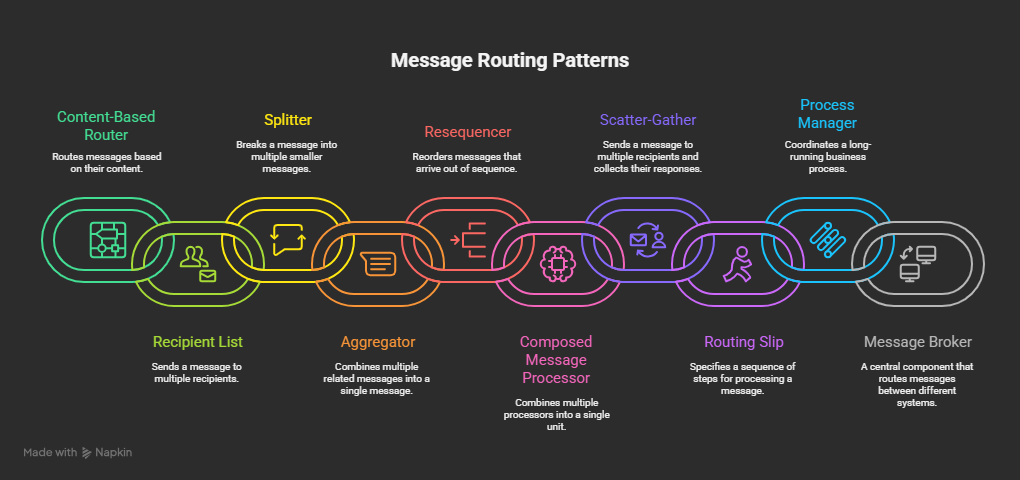
🔁 1. Content-Based Router
✅ Scenario: Routes messages to different destinations based on data within the message.
📘 Use Case: A retail platform routes orders to “Books”, “Electronics”, or “Clothing” queues depending on the order category.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Message received by Logic App
- Evaluated for
order.category - Routed to the appropriate Service Bus queue
⚙️ Component Roles:
- APIM: Receives orders from external clients
- Logic App: Evaluates content and applies conditional logic
- Service Bus: Routes to department queues
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Order API] → [APIM] → [Logic App]
├──> Queue: Books
├──> Queue: Electronics
└──> Queue: Clothing👥 2. Recipient List
✅ Scenario: Sends a message to multiple recipients determined dynamically at runtime.
📘 Use Case: When a customer places a high-value order, notify compliance, finance, and fulfillment teams simultaneously.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Logic App checks value of order
- Retrieves recipient list from config or Key Vault
- Sends notifications to each target
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Orchestrates looping logic
- Key Vault / Blob Storage: Stores dynamic recipients
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Trigger: High-Value Order] → [Logic App - ForEach]
├──> Notify Compliance
├──> Notify Finance
└──> Notify Fulfillment🔪 3. Splitter
✅ Scenario: Breaks a single composite message into multiple individual messages for processing.
📘 Use Case: A shipment update contains 100 parcels. Each parcel must be processed independently.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Logic App parses JSON array
- Iterates over each item and publishes to queue
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Implements ForEach
- Service Bus Queue: Distributes messages
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Composite Shipment JSON] → [Logic App - ForEach Item]
→ [Service Bus Queue]🧩 4. Aggregator
✅ Scenario: Combines multiple related messages into a single message.
📘 Use Case: A claims processor waits for 3 documents — ID proof, incident photo, and doctor report — before initiating assessment.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Messages stored in Cosmos DB
- Function App monitors if all required parts have arrived
- When complete, Logic App aggregates and processes claim
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Triggers aggregation
- Cosmos DB: Stores document states
- Function App: Checks for readiness
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Document Uploads] → [Cosmos DB]
↓
[Function App → Logic App → Claims System]🔁 5. Resequencer
✅ Scenario: Reorders messages that arrive out of sequence.
📘 Use Case: Ingested IoT device data must be replayed in sequence for auditing.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Messages stored with sequence number
- Logic App or Durable Function reorders based on sequence
- Forwarded in correct order
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Cosmos DB: Stores messages
- Logic App / Durable Function: Orders and forwards
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[IoT Feed] → [Function App → Cosmos DB]
↓
[Logic App: Reorder + Send]🎭 6. Composed Message Processor
✅ Scenario: Splits a message, processes each part, and recombines the result.
📘 Use Case: Onboarding a user requires ID check, background check, and email verification.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Split into parallel branches
- Process each check
- Recombine into onboarding status
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Splits and joins
- Functions: Implement checks
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Signup Message] → [Logic App]
├──> ID Verification
├──> Background Check
├──> Email Verification
↓
[Join → Status API]🧾 7. Scatter-Gather
✅ Scenario: Sends message to multiple recipients, waits for responses, aggregates results.
📘 Use Case: A price comparison engine queries 4 hotel APIs and shows the best available rate.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Logic App sends parallel requests
- Waits for all or first few responses
- Joins and processes best offer
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Logic App: Parallel actions
- HTTP Connectors: Calls APIs
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Request] → [Logic App]
├──> Hotel API A
├──> Hotel API B
├──> Hotel API C
↓
[Aggregate Response → Return]🎯 8. Routing Slip
✅ Scenario: A message defines its own processing steps in sequence.
📘 Use Case: A loan application flows through KYC, risk, and approval teams — in that specific order.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Routing steps defined in metadata
- Each step executes and passes to next
- Flow ends after final task
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Blob / Cosmos DB: Stores routing slip
- Function App: Evaluates and executes steps
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Loan Request + Slip] → [Function App]
↓
Step 1 → Step 2 → Step 3 → Complete⚙️ 9. Process Manager
✅ Scenario: Orchestrates long-running workflows across systems with state tracking.
📘 Use Case: HR onboarding spans 5+ steps — ID creation, device allocation, policy training, etc.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Durable Function starts orchestration
- Each task is triggered in sequence or conditional logic
- Completion logged
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Durable Function (Orchestrator): Maintains flow
- Logic Apps: Execute external tasks
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[HR Trigger] → [Durable Function]
├──> Step A
├──> Step B
└──> Step C🌐 10. Message Broker
✅ Scenario: Central routing hub that decouples senders and receivers.
📘 Use Case: An e-commerce platform pushes stock updates to ERP, analytics, and storefronts simultaneously.
🔄 End-to-End Flow:
- Publisher sends message to Service Bus Topic
- Subscriptions filter by tags
- Each subscriber processes its copy
⚙️ Component Roles:
- Service Bus Topic: Broadcasts event
- Subscriptions: Filter and route
- Logic Apps: Act on events
🛠 Azure Implementation:
[Stock Update] → [Service Bus Topic]
├──> Sub: ERP
├──> Sub: Analytics
└──> Sub: Web Store👉 Up next: Part 3 – Transformation Patterns, including Canonical Data Model, Content Enricher, Filter, Normalizer, and more.